Back
to listing
Back
to listing
Learning Management Systems in Education: Transforming Learning Experiences
LMS in Education: Transforming Learning with Technology
Introduction: The Digital Transformation of Education
Education is in the midst of a profound transformation. Where classrooms once relied solely on physical textbooks and face-to-face instruction, today’s learning environments blend education technology (EdTech) with traditional methods. At the heart of this evolution is the Learning Management System (LMS).
An LMS in education is not just a platform—it’s a comprehensive framework that supports teachers, empowers students, and streamlines administration. From K-12 schools to universities and corporate training programs, LMS platforms are becoming indispensable tools for modern learning.
In this article, we’ll explore what LMS stands for, how it works, its evolution, types, benefits, challenges, and the innovations shaping the future of digital learning.
What Does LMS Stand For in Education?
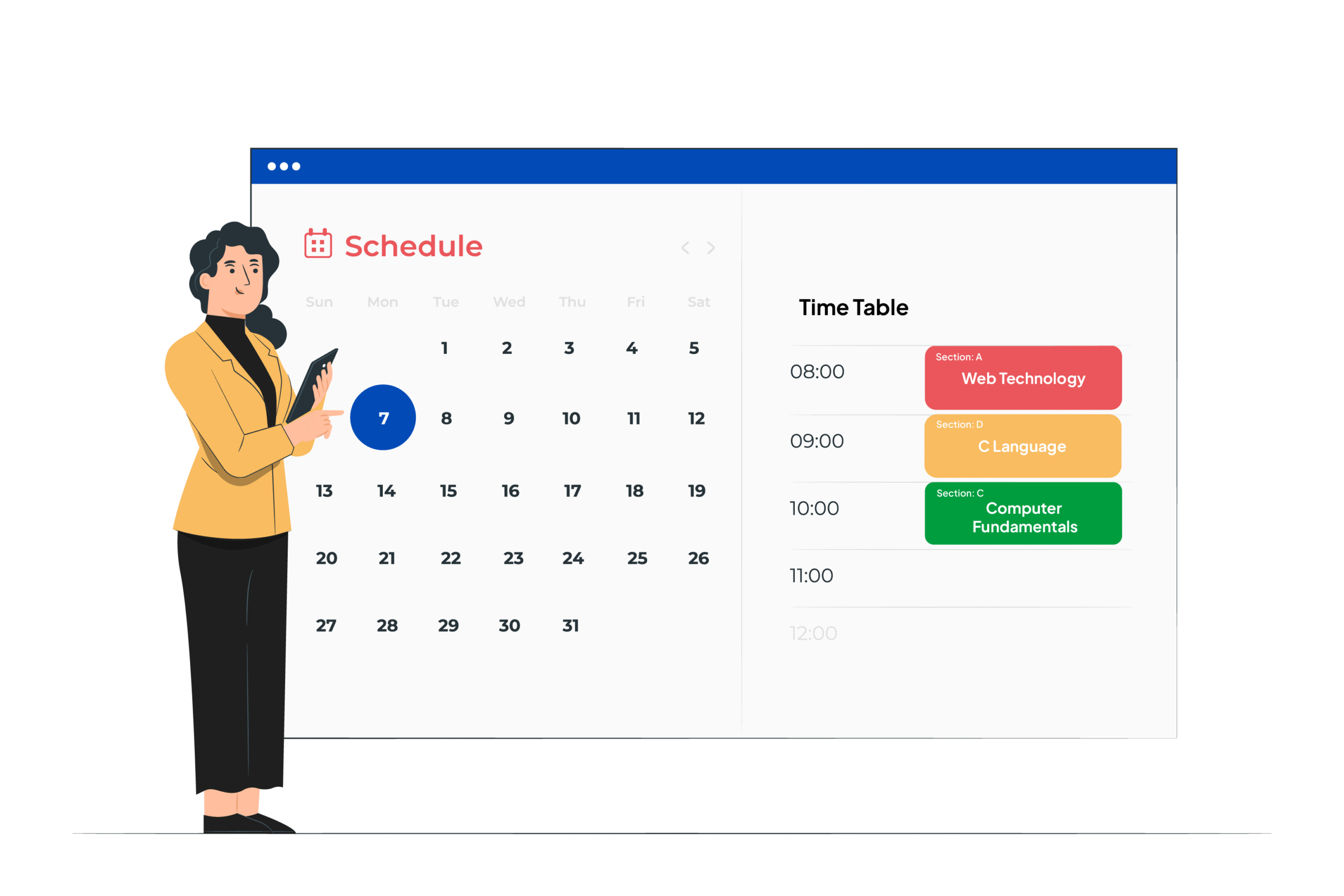
The term LMS stands for Learning Management System. It’s a software platform designed to deliver, manage, and track learning experiences. In practice, this means that educators can design courses, share content, assign homework, and evaluate performance all in one place.
Key highlights of LMS in education:
Centralized Learning Hub: One platform for content, communication, and collaboration.
Flexible Delivery: Supports both online learning and blended classrooms.
Personalization: Tailors lessons to individual learning styles and paces.
Analytics: Tracks student progress with real-time insights.
In short, an LMS is more than just a teaching aid—it’s a cornerstone of education technology that makes learning accessible, interactive, and measurable.
Understanding LMS: Core Concepts and Functions
At its core, an LMS also known in some regions as a Virtual Learning Environment (VLE), is about organizing and delivering knowledge. Whether deployed in schools or higher education institutions, it creates a digital framework where teaching and learning come together.
Core Components of LMS Platforms
Course Management: Design, organize, and publish course materials.
User Management: Control permissions and access for teachers, students, and administrators.
Content Delivery: Share multimedia formats—videos, PDFs, audio, interactive modules.
Assessment Tools: Conduct quizzes, assignments, and exams with automated grading.
Collaboration Features: Enable discussions, group projects, and peer-to-peer communication.
Flexible Learning Modes
Synchronous Learning: Real-time interaction via video conferencing or live chats.
Asynchronous Learning: On-demand access to recorded lectures and self-paced modules.
This flexibility is essential in today’s diverse learning landscape, where students may prefer different styles and schedules.
The Evolution of Learning Management Systems
The history of LMS in education mirrors the broader growth of EdTech:
Early 2000s: Simple repositories for documents and course notes.
Late 2000s: Multimedia features like video and interactive tools emerged.
2010s: Cloud-based LMS platforms made learning scalable and mobile-friendly.
Today: AI and data analytics are driving personalized learning and predictive insights.
One of the biggest shifts came with cloud computing, which reduced infrastructure costs and improved accessibility. Mobile compatibility followed, allowing students to access learning materials from any device.
Now, with artificial intelligence and virtual reality, LMS platforms are moving beyond management—they’re creating truly immersive and personalized educational experiences.
Key Features of Learning Management System
Modern LMS solutions are equipped with a variety of tools that cater to both educators and learners. Some of the most impactful include:
Comprehensive Course Management – Easy course creation, scheduling, and content organization.
User Roles & Permissions – Tailored access for administrators, instructors, and students.
Interactive Content Support – Videos, podcasts, gamification, and simulations.
Assessments & Feedback – Automated grading, progress tracking, and instant feedback.
Communication Tools – Forums, messaging, announcements, and integrated video conferencing.
Analytics & Reporting – Insights on attendance, participation, and performance.
Mobile Learning (mLearning) – Dedicated apps or responsive design for on-the-go learning.
By blending these features, LMS platforms create an ecosystem where learning is not just accessible, but engaging and measurable.
Types of LMS in Education
Choosing the right LMS is crucial, as each type offers unique advantages:
Cloud-Based LMS: Accessible anytime, anywhere. Cost-effective and scalable.
Open-Source LMS: Flexible and customizable but requires IT expertise (e.g., Moodle).
Self-Hosted LMS: Offers maximum control over data and security but comes with higher costs.
Commercial LMS: Subscription-based with vendor support and continuous updates.
Cloud-based LMS, often referred to as a SaaS LMS or web-hosted LMS, is popular due to its accessibility and scalability. As a hosted learning platform, it requires no local installation and allows institutions to focus on teaching rather than infrastructure. This type of cloud learning system is ideal for schools and universities with remote learners or distributed campuses.
LMS Integration with Education Technology
An LMS rarely works alone. Instead, it integrates with broader education technologies to form a complete digital learning ecosystem:
Virtual Classrooms: Platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams integrated into LMS.
Digital Libraries: Seamless access to eBooks, journals, and multimedia.
Assessment Tools: Integration with plagiarism checkers, proctoring software, and adaptive quizzes.
Student Information Systems (SIS): Unified data management for attendance and grades.
This integration ensures that learning is not fragmented but cohesive, making LMS the backbone of modern EdTech strategies.
Benefits of LMS in Education
The benefits of adopting LMS in education are extensive:
For Students
Personalized Learning Paths: Adaptive lessons based on progress.
Anytime, Anywhere Access: Mobile learning and self-paced modules.
Interactive Experiences: Gamified lessons and collaborative projects.
For Educators
Efficiency: Automated grading and attendance tracking.
Organization: Centralized hub for course planning and resource sharing.
Engagement Tools: Quizzes, polls, and discussion forums to drive participation.
For Institutions
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced need for physical materials.
Scalability: Support for thousands of users simultaneously.
Data-Driven Decisions: Analytics to measure learning outcomes and adjust strategies.
Ultimately, LMS platforms enhance student engagement, institutional efficiency, and overall learning outcomes.
Student Engagement and Personalized Learning
LMS platforms support customised learning by allowing educators to design modules that adapt to each learner’s pace and preferences.
Engagement Tools: Discussion forums, live polls, and gamification increase participation.
Personalized Pathways: Students progress at their own pace, focusing on areas where they need improvement.Through data-driven insights, teachers can provide individualized instruction that targets each student’s strengths and areas for growth.
Timely Feedback: Automated grading ensures quick feedback loops.
This student-centered approach encourages deeper involvement and creates a more inclusive educational environment.
LMS for Educators: Streamlining Administration
Educators often juggle multiple roles—teaching, mentoring, and administration. LMS platforms simplify their workload by:
Automating repetitive tasks like grading and attendance.
Providing a digital space for course design and resource organization.
Offering communication tools to stay connected with students and parents.
With these tools, educators can focus more on teaching quality and student interaction instead of administrative burdens.
Best LMS Platforms in Education
Several LMS solutions dominate the global education market, each offering unique features to meet different institutional needs:
EDU: A modern LMS designed for flexibility and scalability, EDU combines intuitive course management with advanced analytics. It emphasizes ease of use, mobile compatibility, and seamless integration with other education technologies—making it a strong choice for institutions aiming to personalize learning at scale.
Moodle: Open-source, customizable, and widely used in higher education for its flexibility and strong community support.
Canvas: User-friendly with robust integration options, making it especially popular among universities.
Blackboard: A comprehensive platform with powerful features for academic and corporate training.
Google Classroom: Free, simple, and widely adopted in K-12 education for its accessibility.
Schoology & Brightspace: Known for collaboration tools, advanced analytics, and strong adoption in K-12 and higher education.
When choosing an LMS, institutions should evaluate their goals, budget, and technical capacity to ensure the platform aligns with long-term educational strategies.
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Implementing an LMS is not just about installation—it requires strategic planning:
Needs Assessment: Identify goals, user needs, and budget.
Stakeholder Involvement: Include educators, administrators, and IT staff in decisions.
Training & Onboarding: Provide robust training for staff and students.
Continuous Evaluation: Gather feedback and refine processes regularly.
Following these steps ensures smoother adoption and maximizes the return on investment.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, LMS platforms bring challenges that must be addressed:
Data Security: Protecting sensitive student and institutional data.
Privacy Compliance: Adhering to laws like GDPR and FERPA.
Accessibility: Ensuring LMS supports diverse learners, including those with disabilities.
Digital Divide: Bridging gaps for students without reliable internet access.
By proactively tackling these challenges, institutions can ensure equitable and safe learning environments.
The Future of LMS in Education
The future of LMS lies in innovation and adaptability. Trends shaping the next wave include:
AI-Powered Personalization: Tailoring learning paths and recommending content.
Immersive Technologies: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) for hands-on simulations.
Microlearning: Bite-sized lessons designed for mobile-first learners.
Data-Driven Predictive Analytics: Identifying at-risk students early for intervention.
These innovations promise to make LMS even more effective in creating engaging, personalized, and inclusive education.
Conclusion: The Lasting Impact of LMS in Education
The role of LMS in education goes far beyond digital convenience. These platforms are reshaping classrooms, empowering educators, and engaging students in ways that traditional methods alone cannot achieve.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of learning will be defined by flexibility, personalization, and innovation—all driven by Learning Management Systems. For institutions committed to excellence, adopting an LMS is not just an option; it’s a necessity for preparing learners for the future.
Ready to Transform Learning with LMS?
Choosing the right LMS can unlock new possibilities for your institution—boosting engagement, streamlining administration, and creating more personalized learning journeys.
Explore EDU today—a next-generation LMS designed to simplify teaching, empower learners, and future-proof education.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an LMS in education and how does it work?
An LMS (Learning Management System) is a digital platform that enables institutions to create, deliver, and manage learning content online. It allows educators to design courses, assign materials, evaluate students, and track performance from a single dashboard.
Modern LMS platforms like EDU ERP combine cloud technology, analytics, and AI to personalize learning paths and make education accessible anytime, anywhere. For schools, colleges, and universities, it simplifies academic management while enhancing student engagement.
What are the main features of a learning management system?
A well-designed LMS provides a comprehensive suite of tools for educators and learners, including:
Course Management: Easy creation and scheduling of learning modules.
Assessment Tools: Online quizzes, automated grading, and progress tracking.
Collaboration Tools: Forums, chat, and video conferencing.
Analytics and Reports: Insights into attendance, performance, and participation.
Mobile Learning: Access via smartphones or tablets for flexibility.
With EDU ERP, institutions can integrate these features into their academic workflows, improving efficiency, engagement, and learning outcomes.
Why should institutions adopt an LMS in today’s educational environment?
Institutions adopt LMS platforms to modernize education delivery, streamline administration, and enable personalized learning.
An LMS supports both online and blended learning models, making it essential for flexible, scalable education.
By implementing an LMS like EDU ERP, institutions can reduce manual workload, enhance collaboration, and align teaching methods with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020—which emphasizes digital and skill-based learning.
How does an LMS integrate with other education technologies or ERP systems?
Modern LMS platforms are designed to integrate seamlessly with student information systems (SIS), ERP modules, and virtual classroom tools.
For instance, EDU ERP’s LMS connects with admissions, attendance, assessments, and finance modules, creating a unified digital learning ecosystem.
This integration ensures that academic and administrative data are synchronized in real time—improving efficiency, transparency, and institutional control.
What are the latest trends shaping the future of LMS in education?
The next generation of LMS platforms is being driven by AI, data analytics, and immersive technologies.
Emerging trends include:
AI-powered personalization to adapt content to student progress.
Gamified learning to increase motivation and engagement.
Microlearning modules designed for mobile-first users.
AR and VR integration for experiential learning.
Predictive analytics for identifying at-risk students early.
Platforms like EDU ERP are already adopting these innovations, helping institutions move toward data-driven, inclusive, and future-ready learning ecosystems.